1. Executive Summary
The OTC hearing aid market is transforming the audiology industry. FDA deregulation in 2022 opened doors for direct-to-consumer sales, disrupting traditional channels dominated by audiologists. New entrants (Bose, Jabra, Eargo) leverage DTC models, while incumbents (Sonova, Demant, WS Audiology) adapt through M&A and partnerships.
Key findings:
- Price erosion: OTC devices average $800-$1,500, undercutting traditional aids ($2,000-$6,000).
- Channel shift: Online (Amazon, Best Buy) and pharmacies (CVS, Walgreens) now account for 35% of OTC sales.
- Tech race: AI-driven self-fitting and Bluetooth connectivity are now table stakes.
2. Market Definition and Scope
Primary Focus: U.S. market (80% of global OTC sales). Secondary analysis of EU (slower adoption) and Asia (nascent but growing).
Timeframe: Post-FDA rule (2022–2027).
3. Regulatory Landscape
FDA’s 2022 Rule:
- Allows OTC sales for mild-to-moderate hearing loss.
- No Rx required, but mandates sound pressure limits and labeling.
Global Contrasts:
- EU: Stricter (Class IIa medical devices).
- Asia: Hybrid models (e.g., Japan’s “quasi-OTC”).
Risk: Quality concerns may trigger future FDA recalls .
4. Manufacturer Competitive Dynamics
Incumbents vs. Disruptors
| Traditional Players | New Entrants |
|---|---|
| Sonova (Phonak) | Bose (SoundControl) |
| Demant (Oticon) | Jabra (Enhance Plus) |
| WS Audiology (Signia) | Eargo (FDA-cleared OTC) |
Strategies:
- Incumbents: Launch “bridge” products (e.g., Phonak’s Costco partnership).
- Disruptors: Focus on DTC + tech (e.g., Bose’s self-fitting app).
5. Channel Disruption and Adaptation
Audiologists (Declining Fittings?)
- -15% fittings since 2022 (ASHA data).
- Shift to hybrid models (e.g., “remote tuning” fees).
Online Retailers (Amazon, Best Buy)
- Amazon’s private-label OTC aids (under $500).
- Best Buy’s Geek Squad support for DIY setups.
Pharmacies (CVS, Walgreens)
- Store-brand OTC aids (e.g., CVS Health Hearing).
6. Consumer Behavior Shifts
Drivers:
- Price (60% cite affordability).
- Accessibility (no clinic visits).
Barriers:
- Perceived quality (“Is OTC as good?”).
- Lack of professional support (33% return rate).
7. Pricing and Margin Pressures
| Type | Avg. Price | Margin |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional | $4,000 | 55% |
| OTC | $1,200 | 35% |
| DTC Disruptors | $800 | 25% |
Manufacturer Response:
- Cost-cutting: Shift production to China OEMs (e.g., China Hearing Aids Factory).
- Premium OTC: Add Bluetooth, AI noise reduction to defend margins.
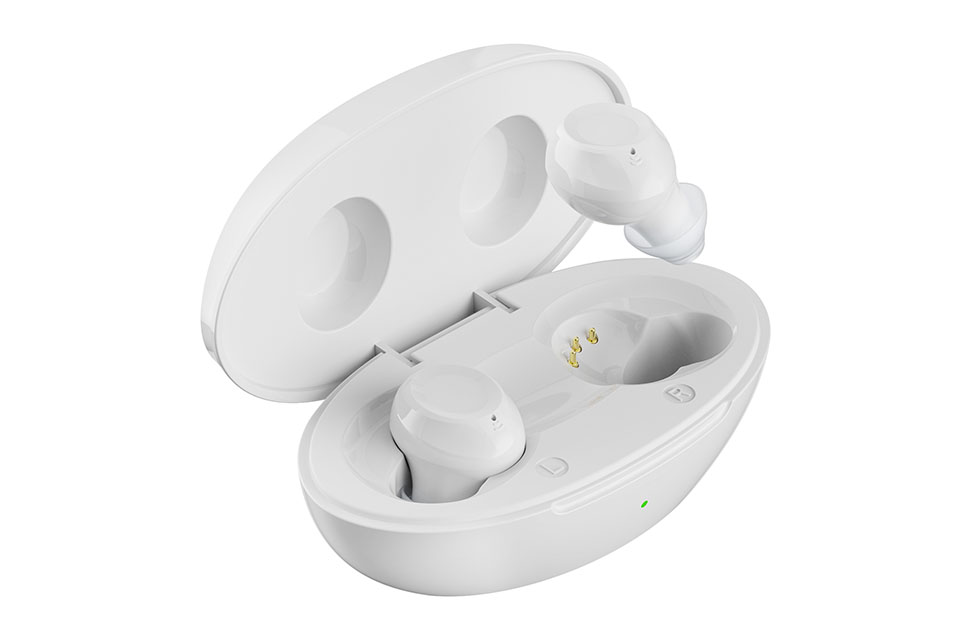

8. Technology and Product Differentiation
Key Features:
- Self-fitting algorithms (e.g., App Control Hearing Aids).
- Rechargeability (90% of new OTC models).
- TWS (True Wireless Stereo) for streaming.
Figure 3: AI-driven sound processing in OTC devices [4].
9. Strategic Responses from Incumbents
- M&A: Sonova acquired Sennheiser’s hearing biz for consumer tech expertise.
- Vertical Integration: Demant now owns online retailer Audious.
10. Risks and Unintended Consequences
- Quality issues: 12% of OTC aids fail FCC testing.
- Audiologist backlash: Lobbying for state-level Rx requirements.
11. Future Outlook and Projections
5-Year Trends:
- Subscription models ($30/month for upgrades).
- Health tech integration (Apple Hearing Aid mode?).
Wildcard: FDA re-regulation if safety complaints spike.
Why Partner with a Hearing Aid OEM?
For brands entering OTC, China Hearing Aids Factory offers:
- ISO-certified production (3M units/year).
- Bluetooth/DSP chip-ready designs.
- Private-label ODM for DTC brands.
Act now—OTC is reshaping hearing care.







